
In today’s digital world, businesses must harness the power of analytics to facilitate growth, efficiency, and profitability. Analytics is the methodical use of data, quantitative analysis, and statistical techniques to make well-informed decisions and solve problems. It enables organizations to identify trends, patterns, and insights, allowing them to make data-driven decisions that enhance overall performance.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into different types of analytics, their importance, data worth paying attention to, and how to utilize analytics in different areas of your business.
Types of Analytics
There are four primary types of analytics, each serving distinct purposes and providing valuable insights for businesses:
Descriptive Analytics
Descriptive analytics forms the basis of business analytics. It involves the analysis of historical data to comprehend past events and trends. Descriptive analytics helps businesses identify patterns and relationships in their data, enabling them to understand what has happened and why.
Techniques used in descriptive analytics include data visualization, reporting, and descriptive statistics.
- Data visualization techniques, such as charts and graphs, allow businesses to present complex data in an easily digestible format, while reporting helps communicate the findings to stakeholders.
- Descriptive statistics, including measures of central tendency and dispersion, summarize data and facilitate the identification of patterns and trends.
Diagnostic Analytics
Diagnostic analytics aims to uncover the root causes of observed trends and patterns. By analyzing historical data, businesses can determine the factors that led to particular outcomes.
Diagnostic analytics techniques include data mining, drill-down analysis, and correlation analysis.
- Data mining involves the exploration and analysis of large datasets to discover hidden patterns, correlations, and anomalies.
- Drill-down analysis allows businesses to investigate the details of aggregated data to pinpoint specific issues or events.
- Correlation analysis helps in identifying the relationships between variables and understanding how they influence each other.
Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics employs historical data and statistical models to forecast future events and trends. By leveraging machine learning algorithms, predictive analytics can identify patterns and relationships in data that may not be readily apparent. This type of analytics assists businesses in anticipating future outcomes and making proactive decisions.
Techniques employed in predictive analytics include regression analysis, time series analysis, and data mining.
- Regression analysis helps predict the relationship between dependent and independent variables, while time series analysis focuses on analyzing data points collected over time to identify trends and make predictions.
- Data mining, as previously mentioned, can also be used for predictive purposes.
Prescriptive Analytics
Prescriptive analytics goes a step further by suggesting specific actions to optimize business outcomes based on the predictions made.
This type of analytics combines predictive models, business rules, and optimization techniques to recommend the best course of action for a given situation.
- Prescriptive analytics is often used in conjunction with simulation and scenario analysis to evaluate the potential impact of different decisions.
- Simulation involves the creation of models that mimic real-world situations, allowing businesses to test various scenarios and strategies, while scenario analysis explores the potential outcomes of multiple decision pathways.
Importance of Analytics for Business
The use of analytics is vital for businesses for several reasons:
Enhanced Decision-Making
Analytics provides businesses with data-driven insights, enabling them to make informed decisions based on facts rather than intuition. This leads to better decision-making and ultimately better business outcomes. By incorporating analytics into their decision-making processes, businesses can mitigate the risks associated with biased or uninformed decisions, resulting in more effective strategies and increased likelihood of success.
Improved Operational Efficiency
Analytics can help identify areas of inefficiency within a business, such as process bottlenecks, underperforming resources, or excessive costs. By addressing these issues, businesses can streamline their operations, reduce waste, and improve overall efficiency. For example, process mining techniques can be used to analyze and visualize end-to-end processes, uncovering inefficiencies, redundancies, and non-compliance with predefined standards. Once these issues are identified, businesses can implement corrective measures, such as process automation or re-engineering, to enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs.
Increased Revenue and Profitability
Analytics can help businesses identify new revenue opportunities and optimize pricing strategies. By understanding customer behavior, market trends, and competitive forces, businesses can tailor their offerings to better meet customer needs and maximize revenue and profitability. For instance, market basket analysis can reveal which products are frequently purchased together, enabling businesses to create targeted promotions or bundle offers to increase sales. Additionally, price optimization techniques can be used to determine the optimal price points that maximize revenue while maintaining customer satisfaction.
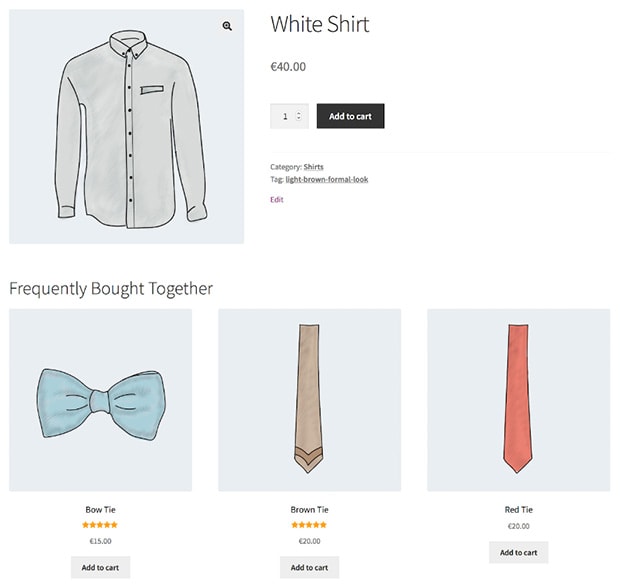
Risk Management
Analytics can help businesses identify and mitigate risks, such as potential supply chain disruptions, financial risks, or regulatory compliance issues. By proactively addressing these risks, businesses can minimize potential losses and protect their reputation. For example, predictive analytics can be used to forecast potential supply chain disruptions, allowing businesses to develop contingency plans or identify alternative suppliers in advance. Similarly, financial risk models can be employed to assess credit risk, interest rate risk, or currency risk, enabling businesses to implement effective risk mitigation strategies.
Enhanced Customer Experience
Through the analysis of customer data, businesses can gain insights into customer preferences, behaviors, and pain points. This information enables businesses to tailor their products, services, and marketing efforts to better meet customer needs and enhance the overall customer experience. For example, customer segmentation techniques can be used to group customers based on their needs, preferences, or behaviors, allowing businesses to deliver personalized marketing messages, offers, or recommendations. Additionally, sentiment analysis can be employed to analyze customer feedback from various channels, such as social media, surveys, or online reviews, enabling businesses to identify and address customer concerns promptly.
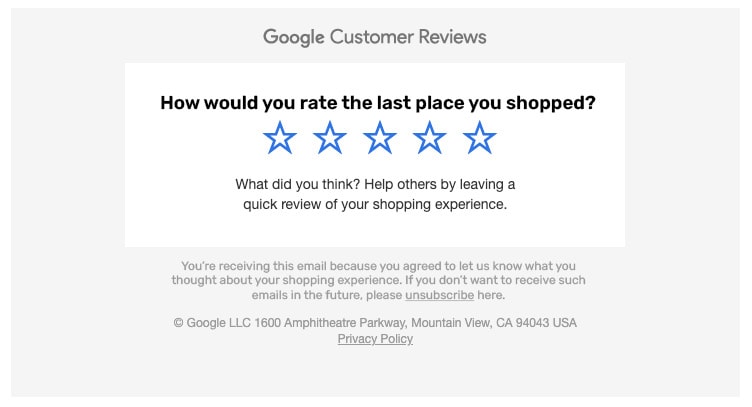
Identifying Relevant Data
To effectively utilize analytics, businesses must first identify the data that is most relevant to their goals and objectives. This may include:
Financial Data
Financial data, such as sales, revenue, and expenses, is crucial for understanding a business’s performance and profitability. Analyzing this data can help identify trends, opportunities for growth, and potential areas for cost reduction. For instance, businesses can employ financial ratio analysis to assess their financial health, benchmark their performance against industry peers, or identify potential liquidity, solvency, or profitability issues.
Customer Data
Customer data includes information on customer demographics, preferences, behaviors, and purchasing patterns. This data is essential for understanding customer needs and preferences, enabling businesses to tailor their products, services, and marketing efforts to better resonate with their target audience. Techniques such as cohort analysis, customer lifetime value (CLTV) estimation, or churn prediction can be employed to gain insights into customer behavior and inform customer acquisition, retention, or upselling strategies.
Operational Data
Operational data encompasses information related to a business’s internal processes, such as production levels, inventory levels, and employee performance. Analyzing this data can help identify areas of inefficiency and opportunities for process improvement. For example, businesses can use throughput analysis to assess the capacity and efficiency of their production processes, while inventory analysis can help optimize inventory levels, reduce stockouts, or minimize carrying costs.
Market Data
Market data includes information on competitors, industry trends, and economic conditions. By analyzing market data, businesses can gain insights into the competitive landscape and make informed decisions about their market positioning and strategy. Techniques such as competitor analysis, market segmentation, or trend analysis can be employed to assess market dynamics, identify opportunities or threats, and inform strategic planning.
Social Media Data
Social media data comprises information on customer sentiments, opinions, and preferences expressed on various social media platforms. This data can help businesses understand customer perceptions, identify potential issues, and improve their online presence. Social media analytics tools can be used to track engagement metrics, such as likes, shares, comments, or followers, and identify the content or campaigns that resonate most with the target audience. Additionally, sentiment analysis can be employed to gauge customer sentiment towards a brand, product, or service, enabling businesses to address negative feedback or capitalize on positive perceptions.
Utilizing Analytics in Different Areas of Business
Analytics can be applied to virtually all aspects of business, driving improvements in efficiency, effectiveness, and profitability. Here are some examples of how analytics can be utilized in different areas of your business:
Sales and Marketing
Analytics can be used to segment customers based on their preferences, purchase history, and demographic information. This enables businesses to tailor their marketing messages and offers to different customer segments, resulting in more effective marketing campaigns and increased sales. Techniques such as lead scoring, conversion rate optimization, or marketing attribution can be employed to assess the effectiveness of marketing efforts, identify high-value prospects, or allocate marketing budgets more efficiently.
Supply Chain Management
By analyzing supply chain data, businesses can identify potential bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and risks. This enables them to optimize their supply chain processes, minimize disruptions, and reduce costs. Techniques such as demand forecasting, inventory optimization, or supplier performance analysis can be used to improve supply chain visibility, ensure timely delivery of products, or evaluate supplier reliability and risk.
Human Resources
Analytics can be used to analyze employee performance data, identify high-performing individuals, and uncover skill gaps within the organization. This information can be used to inform hiring decisions, employee training and development programs, and performance management strategies. Techniques such as workforce analytics, talent analytics, or employee engagement analysis can be employed to assess employee productivity, turnover, or satisfaction, and inform HR policies and practices.
Finance
Financial analytics can help businesses assess their financial performance, identify areas for cost reduction, and optimize pricing strategies. This can lead to increased profitability and improved financial management. Techniques such as budget variance analysis, cost-volume-profit analysis, or financial risk modeling can be employed to monitor financial performance, evaluate the impact of different cost structures or pricing strategies, or assess financial risk exposure.
Product Development
By analyzing customer feedback, market trends, and competitor offerings, businesses can identify opportunities for product innovation and improvement. This enables them to stay ahead of the competition and meet evolving customer needs. Techniques such as feature importance analysis, product portfolio analysis, or conjoint analysis can be employed to prioritize product features, assess the performance of a product line, or determine customer preferences for product attributes.
Data-driven, business environmental analytics have become a crucial tool for driving growth, efficiency, and profitability. By understanding analytics, their importance, the data to pay attention to, and how to utilize analytics in your organization can empower you to make informed decisions, optimize processes, and ultimately achieve better outcomes.
Investing in analytics capabilities and fostering a data-driven culture will undoubtedly yield long-term benefits in the increasingly competitive global market. As analytics tools and techniques continue to evolve, businesses that stay abreast of these developments and embrace the power of analytics will be well-positioned to thrive in the future.
Do you have questions about your business and analytics? We’d love to help! Please reach out to the Digital Link Team! You may also be interested in checking out our collection of free online tools you can use for your business.
Liked this article?
We are adding more useful articles to our blog every week! Join our subscribers to stay up to date on digital security, marketing, and social media trends.
By entering your email, you agree to receive our monthly newsletter. You can unsubscribe at any time!


